Published
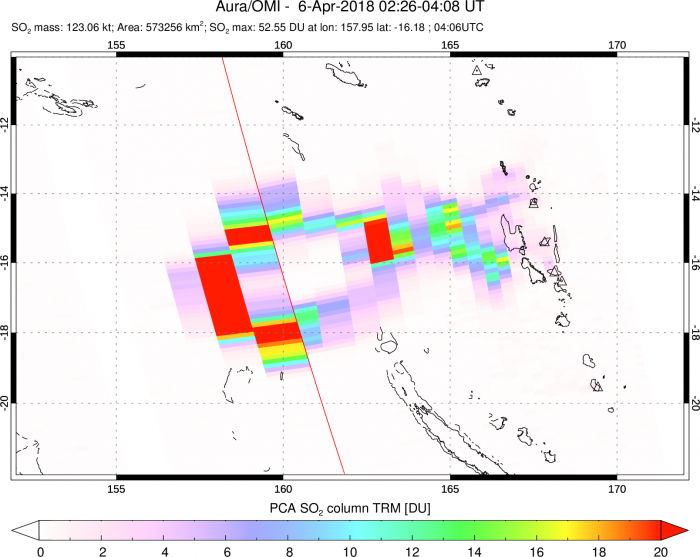
This volcanic SO2 plume data from the Aoba volcano (Vanuatu) explosive eruption on April 5 2018 was retrieved using the Ozone monitoring Instrument (OMI) operational Principal Component Analysis (PCA) algorithm (OMSO2) on April 6.
Volcanic SO2 measured by satellite UV sensors allows tracking fast movements of volcanic ash clouds , which present hazard to aviation. In large explosive eruptions volcanic SO2 can be injected directly into lower stratosphere where it converts to long-lived sulfate aerosols, which have climate and chemistry effects.